- Medial Rectus Definition
- Medial Rectus And Inferior Oblique Dmg Pain
- Medial Rectus And Inferior Oblique Dmg Exercises
- Medial Rectus Function
This video demonstrates a bilateral medial recession + inferior oblique recession surgery in a 13-year-old female patient, who had a V-Pattern esotropia. Surgery location: on-board the Orbis Flying Eye Hospital in Binh Dinh, Vietnam. Rudolph Wagner, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School Transcript (To translate please select your language to the right of this Continue. The inferior division innervates the medial rectus, the inferior rectus, and the inferior oblique muscles. To reach these muscles, the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve runs medially and inferiorly, dividing into three branches (Figure 12). One branch enters the medial rectus muscle and the second branch enters the inferior rectus muscle, both on their conal surfaces; a third.
- Entrapment of an inferior rectus or inferior oblique in a floor fracture are less likely to resolve spontaneously than entrapment of a medial rectus or superior oblique (Figure 12). The edema and ecchymosis around the trochlear complex likely prevents the movement of the superior oblique as well, causing the traumatic Brown’s syndrome.
- When the oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve III) is damaged, a palsy in the medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, and/or inferior oblique muscle(s) may occur. If all of these muscles are affected, the effected eye will be turned outward and downward (due to unopposed action of the lateral rectus and superior oblique muscles).
Click to see full answer.
Then, what does the superior oblique muscle of the eye do?
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit (i.e. from beside the nose) which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular muscle innervated by the trochlear nerve (the fourth cranial nerve).
Additionally, is the inferior oblique muscle vertical or horizontal? When the eye is adducted, the oblique muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the inferior oblique muscle, while depression is due to the action of the superior oblique muscle. The oblique muscles are also primarily responsible for torsional movements.

Medial Rectus Definition
how do you test for superior oblique?
Medial Rectus And Inferior Oblique Dmg Pain
Clinical SignificanceInstead, as mentioned above, the superior oblique is tested by having the patient look down and in. By canceling the action of the inferior rectus muscle via contraction of the medial rectus, one can isolate the action of the superior oblique.
Medial Rectus And Inferior Oblique Dmg Exercises
What are the muscles that move the eye?
Medial Rectus Function
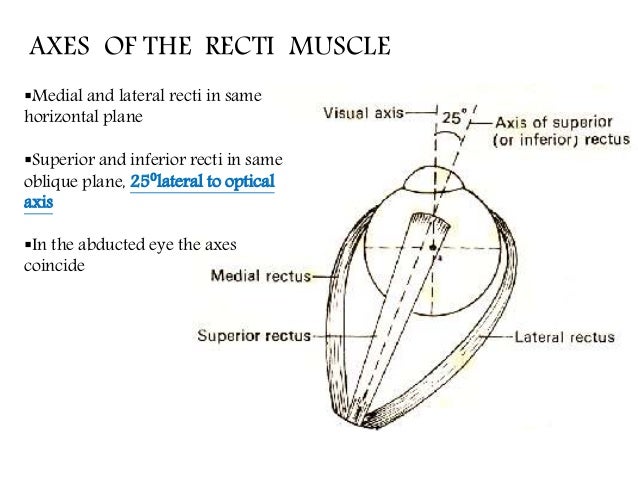
Eye muscle anatomy. There are six extraocular muscles that move the globe (eyeball). These muscles are named the superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus, medial rectus, superior oblique, and inferior oblique.